In Perfect Competition the Marginal Revenue of an Individual Firm
The profit-maximizing level of output is where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. In Prefect competition every firm sells its output at a given price and can sell as much as it likes at this price.
Perfect Competition Economics Help
72 In perfect competition at al levels of output the market price is the same as the firms ________.

. D exceeds the price of the product. In a perfect competition firms produce an output quantity where the marginal cost Marginal Cost The Marginal Cost of Production is the cost to provide one additional unit of a product or service. Equals the price of the product.
Question 33 1 point In perfect competition the marginal revenue of an individual firm O is positive but less than the price of the product. Given the prices a competitive firm sells any amount of quantity. The market price of the product is 150 and the minimum possible average variable cost is 1.
Marginal Revenue Marginal Cost MR MC Rule or Profit Maximization Definition. 29 30In the case of a perfectly competitive firm the Afirms marginal revenue exceeds the price of the product. Module 11 - Perfect Competition 1.
Marginal revenue refers to change in total revenue when output and sales volume is changed by one unit. 71 In perfect competition the marginal revenue of an individual. The marginal cost of the product at the current output level of 500 units is 150.
To maximize profits the firm should. Conceptual 29 In the case of a perfectly competitive firm the A price of the product falls sharply when the quan- tity the firm sells doubles. All producers are price takers and cannot influence the price.
As we know that Perfect competition is a market situation in which each seller is so. In perfect competition the marginal revenue of an individual firm. QUESTION In perfect competition the marginal revenue of an individual firm equals the price of the product is zero is positive but less than the price of the product is greater than the price of the product QUESTION 7 How a tax burden is shared between consumers and producers in a market is determined by O the governments decision on whom to place the.
In perfect competition the marginal revenue of an individual firm. Bis positive but less than the price of the product. The profit maximising condition for a perfectly competitive firm.
Any variation in its output will have a negligible effect on the total supply and effectively the market price that the effect can safely be assumed to be 0. The profit-maximizing level of output is where the difference between total revenue and total cost is the greatest. Cexceeds the price of the product.
A firm under perfect competition faces an infinitely elastic demand curve or we can say for an individual firm the price of the commodity is given in the market. D exceeds the price of the product. Thus in perfect competition MR AR or P.
A perfectly competitive firm is a price taker firm with a large number of buyers and sellers. Now we will discuss about Average revenue and Marginal revenue under perfect competition in detail -. Characteristics of Perfect Competition Perfect competition-a market structure characterized by the interaction of large numbers of buyers and sellers in which the sellers produce a standardized or homogeneous product-These sellers are price takers can sell as much output as they choose to produce at the market price adn have the ability to.
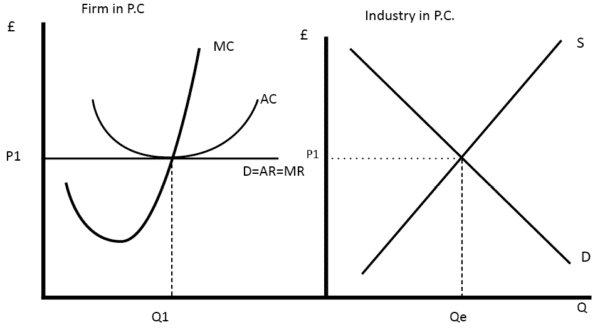
The marginal revenue curve is a horizontal straight line at the given prices which means that marginal revenue and prices are the same PMC. Hence the firms average and marginal revenue become constant and equal. Is the same as its demand curve.
As mentioned before a firm in perfect competition faces a perfectly elastic demand curve for its productthat is the firms demand curve is a horizontal line drawn at the market price level. A perfectly competitive firm earns a profit when price is. E equals the price of the product.
A firm sells a product in a perfectly competitive market. B many firms producing goods that differ somewhat. Is less than its total revenue.
The profit maximising condition for a perfectly competitive firm is where price P equals marginal cost MC. The corresponding AR and MR curve is one and the same and horizontal to the X-axis. In perfect competition the marginal revenue of an individual firm Select one.
A equals the price of the product b is positive but less than the price of the product. D many firms producing identical goods. D exceeds the price of the product.
They simply accept the singular price determined in the market. Another way is using marginal revenue and marginal cost. In perfect competition the marginal revenue of an individual firm.
B is positive but less than the price of the product. B is positive but less than the price of the product. B change in the firms total revenue equals the price of the product multiplied by the change in quantity sold.
In perfect competition the marginal revenue of an individual firm - C equals the price of the product. It is addition to total revenue when output is increased by one unit. The marginal revenue curve is a horizontal straight line at the given prices which means that marginal revenue and prices are the same PMC.
The firm may choose to sell additional output at the same industry price and thus the marginal revenue. The economic profit of a perfectly competitive firm. Given the prices a competitive firm sells any amount of quantity.
Perfect competition is an industry with. 29In perfect competition the marginal revenue of an individual firm Aequals the price of the product. Economics questions and answers.
C a few firms producing goods that differ somewhat in quality. Is positive but less than the price of. O exceeds the price of the product.
QUESTION 9 In perfect competition the marginal revenue of an individual firm equals the price of the product is zero is positive but less than the price of the product is greater than the price of the product. C equals the price of the product. C firms marginal revenue exceeds the price of the product.
The marginal revenue curve shows the additional revenue gained from selling one more unit. C equals the price of the product. It is a fundamental principle that is of the last unit produced is.
A a few firms producing identical goods. In perfect competition the firms marginal revenue curve. Exceeds the price of the product b.

Pin On Economics Business Finance

Class 11 Economics Notes For Introductory Microeconomics Aglasem Schools Economics Notes Economics Lessons Learn Economics

3 4 2 Perfect Competition Mrshearingeconomics
Economies Free Full Text The Dynamics Of The Profitability And Growth Of Restaurants The Case Of Norway Html
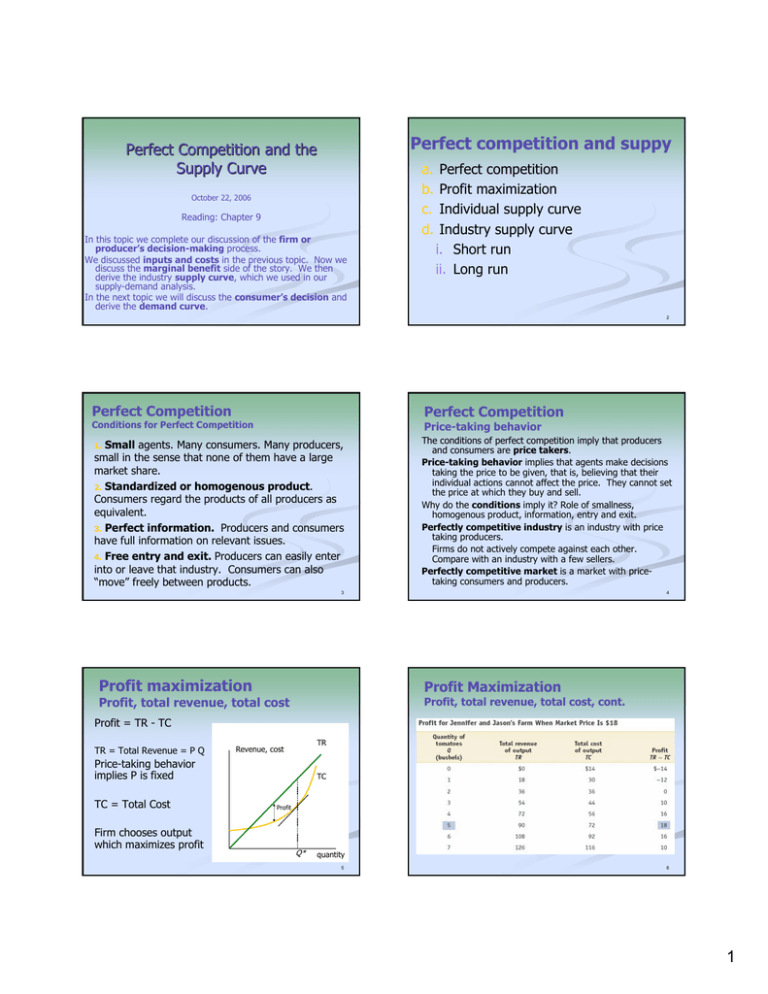
Perfect Competition And Suppy Perfect Competition And The Supply Curve A

3 Types Of Production Function Linear Function Factors Of Production Algebra Equations

Chapter 8 Profit Max And Competitive Supply

Pin On Theory Of Production Microeconomics

Perfect Competition Economics Lessons College Teaching Economics Microeconomics Study

Perfect Competition Economics Lessons College Teaching Economics Microeconomics Study

Perfect Competition Economics Lessons College Teaching Economics Microeconomics Study

Revenue Curve Under Perfect Competition Tutor S Tips
Why Is The Demand Curve Of A Perfectly Competitive Firm Equal To The Marginal Revenue Quora

Page 1 Chapter 10 Quiz Questions 1 In The Model Of Perfect

Types Of Competition And Marginal Revenue Video Khan Academy

Cu Sem Ii Bsc Ttm Tourism Economics 1 Tourism Demand Tourism Industry World Tourism Organization Pubhtml5

Marginal Revenue Marginal Cost And Profit Maximization Ppt Download
