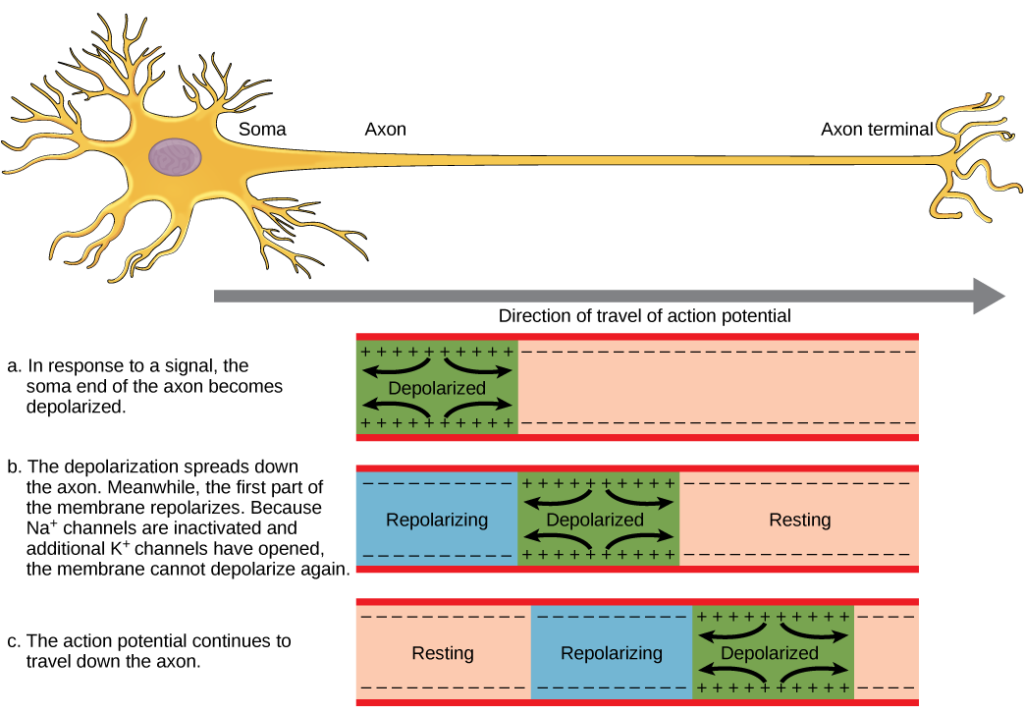
An Action Potential Reaches the Axon Terminal Causing
Acetylcholine receptors function as ligand-gated ion channels. Depolarization overshoot and repolarization.

2 A When Action Potential Reaches The Axon Terminal It Triggers The Download Scientific Diagram
An action potential reaches the axon terminal causing voltage-gated Ca² Calcium ions enter the axon terminal leading to the release of acetylcholine via exocytosis.

. What causes the inside of the membrane to reverse charge and begin the action potential. As calcium flows into the terminal the neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft for 1-2 milliseconds. Neurotransmitter molecules are released from the axon terminal and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron causing either an inhibitory hyperpolarization or an excitatory depolarization.
Voltage-gated CA2- channels. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal the depolarization causes voltage-dependent calcium gates to open. It consists of four phases.
When the action potential reaches the end of the axon the axon terminal it causes neurotransmitter-containing vesicles to fuse with the membrane releasing neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft space between neurons. Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft and calcium ions are pumped out of the axon terminal. This causes the exocytosis of vesicles filled with Neurotransm.
8 Neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft is degraded andor removed to terminate the signal. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon the axon terminal it causes neurotransmitter-containing vesicles to fuse with the membrane releasing neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft space between neurons. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon the axon terminal it causes neurotransmitter-containing vesicles to fuse with the membrane releasing neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft space between neurons.
Acetylcholine binds to receptor sites on the motor end plate. Electric current from action potential open up voltage gated calcium channels. 1 An action potential reaches the end of an axon the synaptic knob.
When the action potential reaches the end of the axon the axon terminal it causes neurotransmitter-containing vesicles to fuse with the membrane releasing neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft space between neurons. The opening of sodium channels in a neuron will cause the interior of the cell to become _____ while the opening of chloride channels will cause the interior of the cell to become _____. Increased calcium ion permeability of the presynaptic terminal cell membrane is caused by an Action potential The neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction is Acetylcholine The neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction increases permeability of the.
The action potential is regenerated due to Na ions moving down the axon depolarizing adjacent. Overview Chemicals released at the axon terminal end Stored in the synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic neuron Released into the. ACH receptors open the associated gated channels Na gated channels Na rushes through the open channels into the muscle cell causing a large depolarization.
The action potential arrives at the axon terminal. Excitatory o Cause depolarization leading to the possibility of the formation of an action potential Inhibitory o Cause hyperpolarization making it more difficult to generate action potential o Neurotransmitters. Is axon hillock the same as axon terminal.
The action potential begins at the axon hillock a swelling located where an axon exits the cell body. Why does hypokalemia cause hyperpolarization. This process of neurotransmitter release is called exocytosis.
This process is called. What are the seven steps of an action potential. This process of neurotransmitter release is called exocytosis.
When an action potential reaches the axon terminal the depolarization causes voltage-dependent calcium gates to open. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal. Calcium channels open allowing calcium ions to enter the axon terminal.
View the full answer. 7 If the membrane depolarization of the postsynaptic cell reaches the threshold of voltage-gated sodium channels an action potential is initiated. 1 When the action potential reaches the axon terminal it causes calcium gates to be opened which results in a burst of neurotransmitter release.
An action potential propagates along the cell membrane of an axon until it reaches the terminal button. Also those changes are the same for every action potential which means that once the threshold is reached the exact same thing happens. Acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft before binding to its receptor located on the motor end plate.
An action potential is caused by either threshold or suprathreshold stimuli upon a neuron. Expert Answer 100 2 ratings Neuronal action potential reaches the axon terminal of neuron 1 which causes calcium voltage-gated channels to open leading to an influx of calcium into the axon terminal of Neuron 1. What causes the inside of the.
Vessicle stimulation neuromodulation exocytosis none of the answers are. Depolarization of the muscle cell membrane. 22 hours agoCalcium rushes into pre-synaptic terminal and initiates exocytosis.
If depolarization reaches -55 mV then the action potential continues and runs all the way to 30 mV at which K causes repolarization including the hyperpolarizing overshoot. As calcium flows into the terminal the neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft for 1-2 milliseconds. Stronger than normal stimulus ie exceeding threshold will initiate an action potential.
Movement of sodium ions into the muscle cell at the neuromuscular junction causes. An action potential reaches the axon terminal causing _____ to open. Choline formed from the breakdown of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft is.
Propagation movement of the Action Potential 1. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon the axon terminal it causes neurotransmitter-containing vesicles to fuse with the membrane releasing neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft space between neurons. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal a depolarization causes voltage-gated _____ channels to open.
How Is Acetylcholine Released From The Axon Terminal Quora
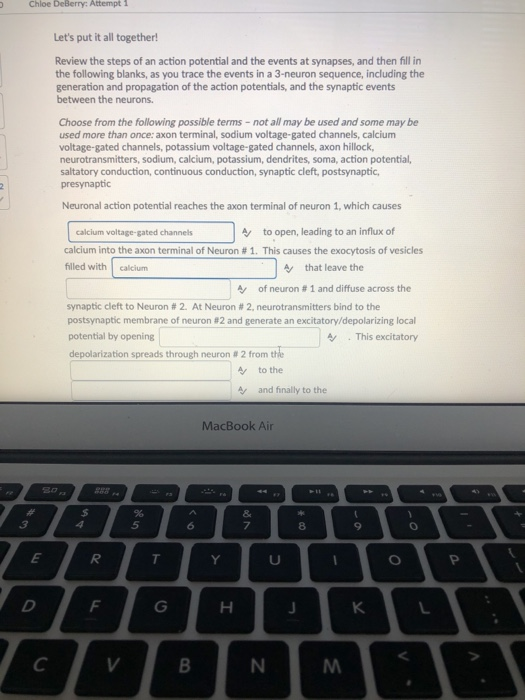
Solved Question 13 19 Points Saved Dindi Let S Put It All Chegg Com

Solved Start Neuronal Action Potential Reaches The Axon Chegg Com
2 A When Action Potential Reaches The Axon Terminal It Triggers The Download Scientific Diagram

Solved Complete Each Sentence With The Correct Word Sodium Chegg Com
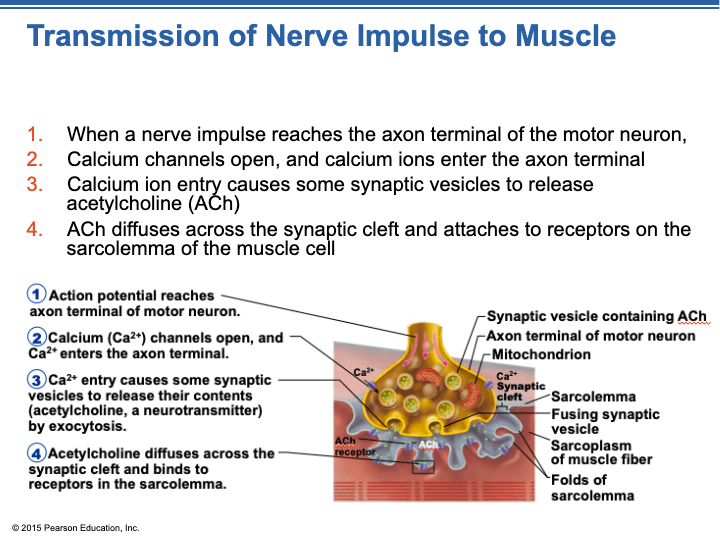
Unit 5 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Activity Quizizz

Solved Question 11 2 Points Save Answer When An Action Potential Reaches The Axon Terminal Most Neurons Release A Chemical Called A Neurotransmitter Which Of The Following Statements Regarding This Process Is Incorrect
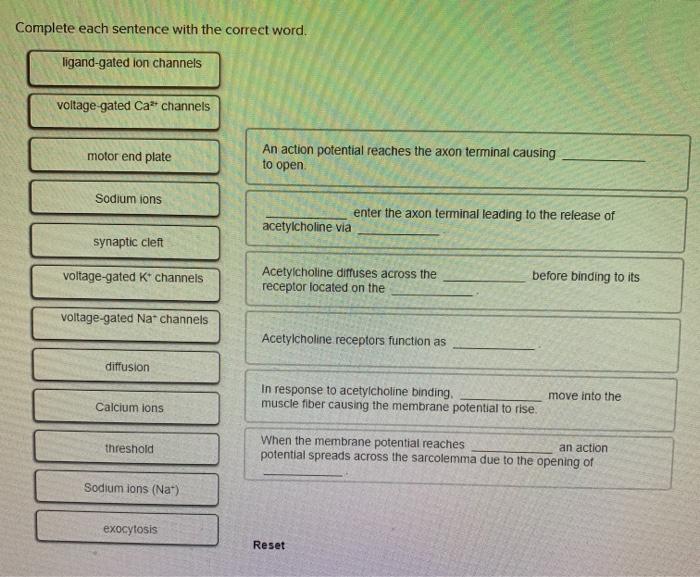
Solved Complete Each Sentence With The Correct Word Chegg Com

Image Showing What Happens When Action Potential Arrives At Axon Terminal Causing Ion Flow And Depolari Basic Anatomy And Physiology Neurons Nurse Study Notes
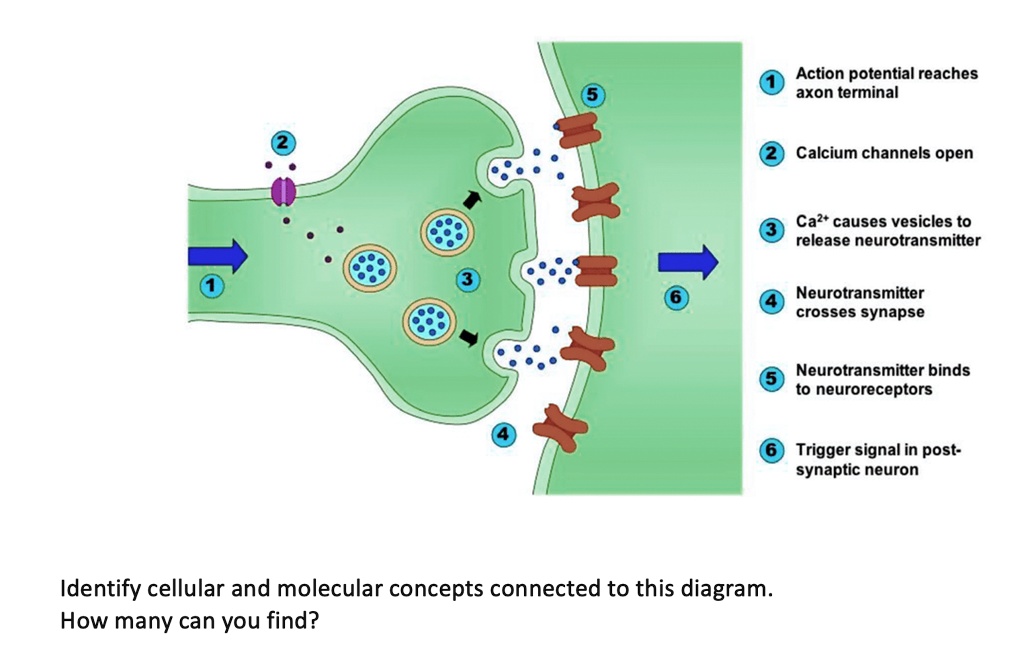
Solved Action Potential Reaches Axon Terminal Calcium Channels Open Ca Causes Vesicles To Release Neurotransmitter Neurotransmitter Crosses Synapse Neurotransmitter Binds To Neuroreceptors Trigger Signal In Post Synaptic Neuron Identify Cellular And

Level 3 Unit 1 Part 18 Neurotransmitter Release Introduction To Neurology

Neuro Week 4 Neuromuscular Junction Action Potentials Nerve Conduction Flashcards Quizlet

When An Action Potential Reaches The Nerve Terminal Voltage Gated Ca Download Scientific Diagram

2 A When Action Potential Reaches The Axon Terminal It Triggers The Download Scientific Diagram
Solved Exsc 202 Connect Assignment 2 Due 2 2 Help Chegg Com
16 2 How Neurons Communicate Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
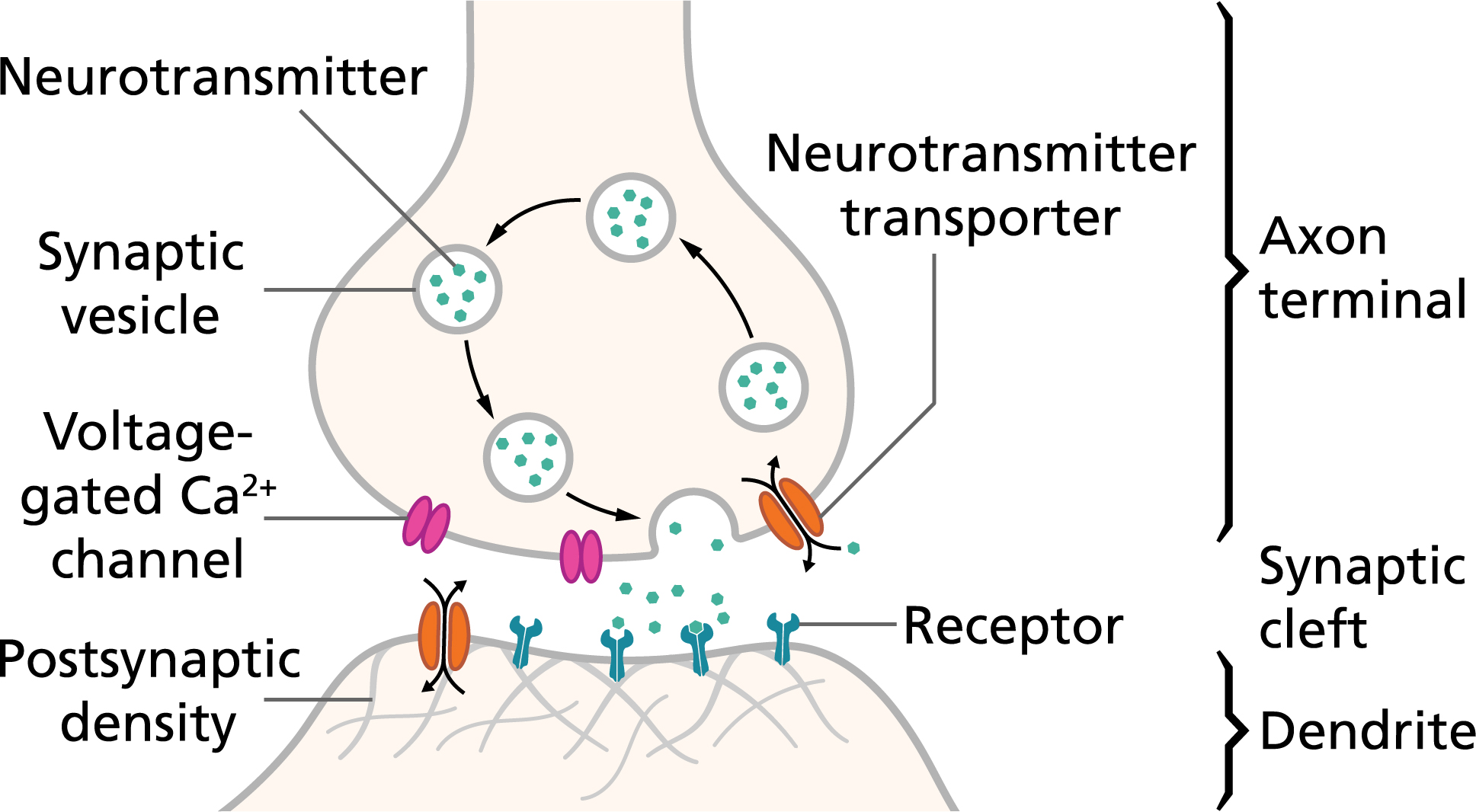
Action Potentials And Synapses Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland